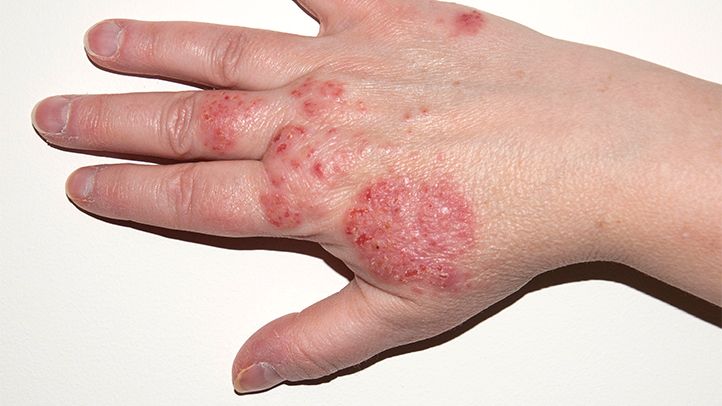
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin. It can vary in severity and often occurs in individuals with a family history of allergic conditions such as asthma or hay fever. Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, irritants, stress, and climate changes. While there is no cure for eczema, treatments such as moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and immunomodulators can help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation, providing relief from itching and discomfort.
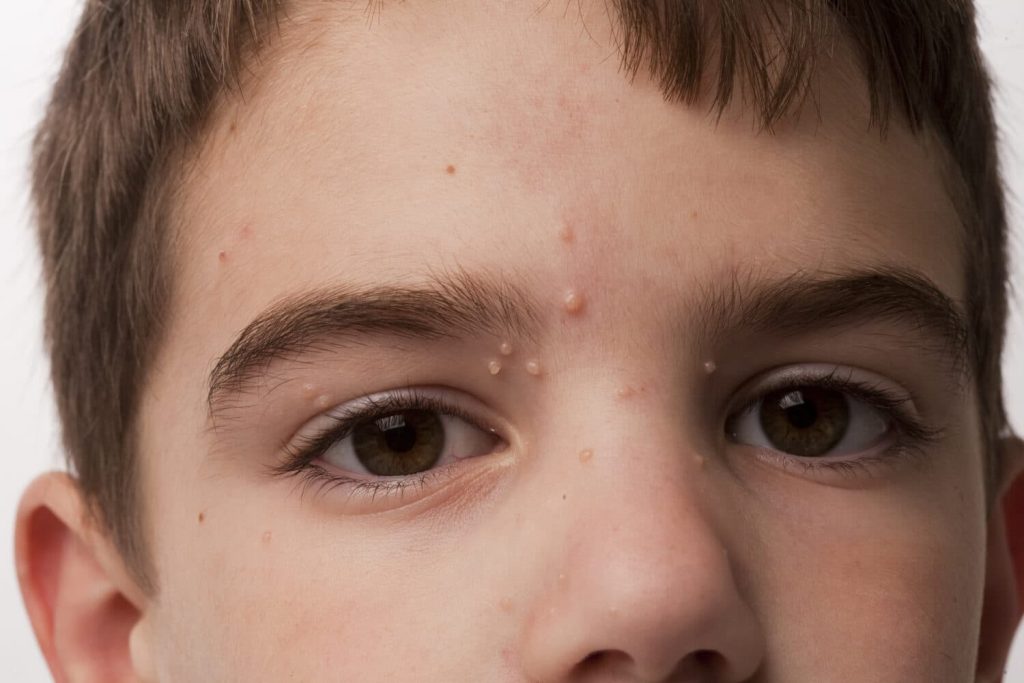
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), which belongs to the poxvirus family. It is characterized by small, flesh-colored, dome-shaped bumps on the skin with a central indentation or “dimple.” Molluscum contagiosum is highly contagious and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by sharing personal items such as towels or clothing. Treatment options include cryotherapy, topical medications, curettage (scraping), or laser therapy to remove the lesions and prevent further spread of the virus.
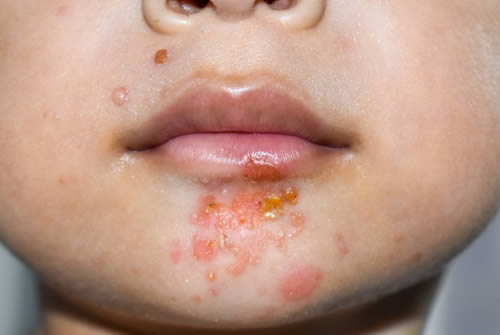
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin infection caused by either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. It is characterized by red sores or blisters that rupture and form honey-colored crusts. Impetigo is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected skin or by sharing contaminated items such as towels or clothing. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antibiotics to kill the bacteria and promote healing of the affected skin.
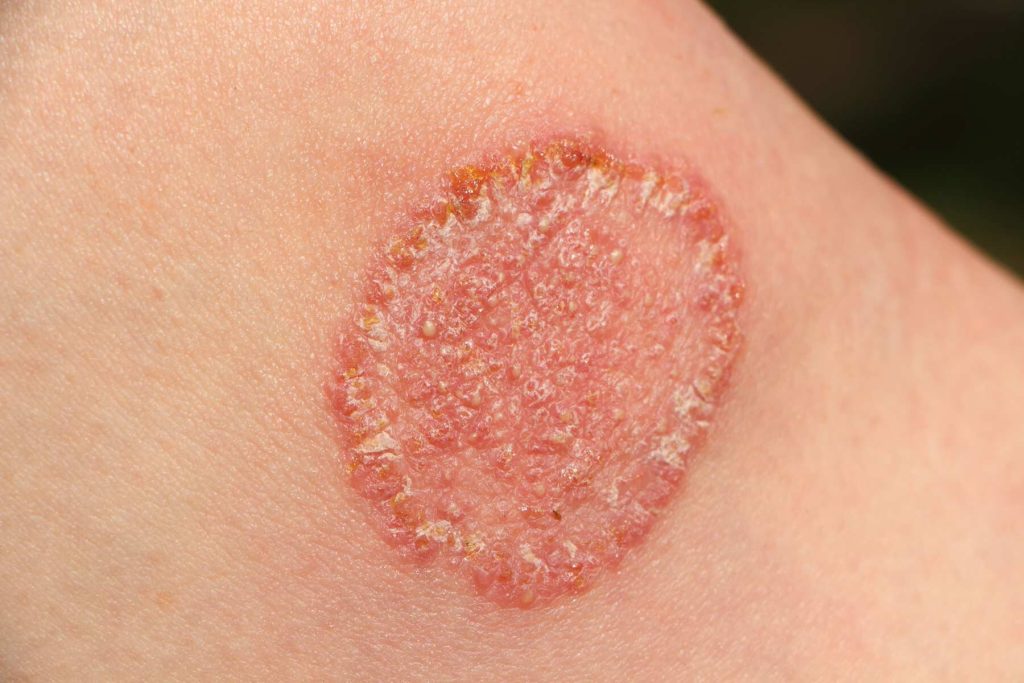
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the skin, also known as dermatophytoses or tinea infections, are caused by various types of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeast, and molds. Common fungal infections include athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), ringworm (tinea corporis), and jock itch (tinea cruris). Fungal infections typically present as red, itchy patches of skin with or without scaling or blistering. Treatment options include antifungal medications, either topical or oral, depending on the severity and location of the infection.
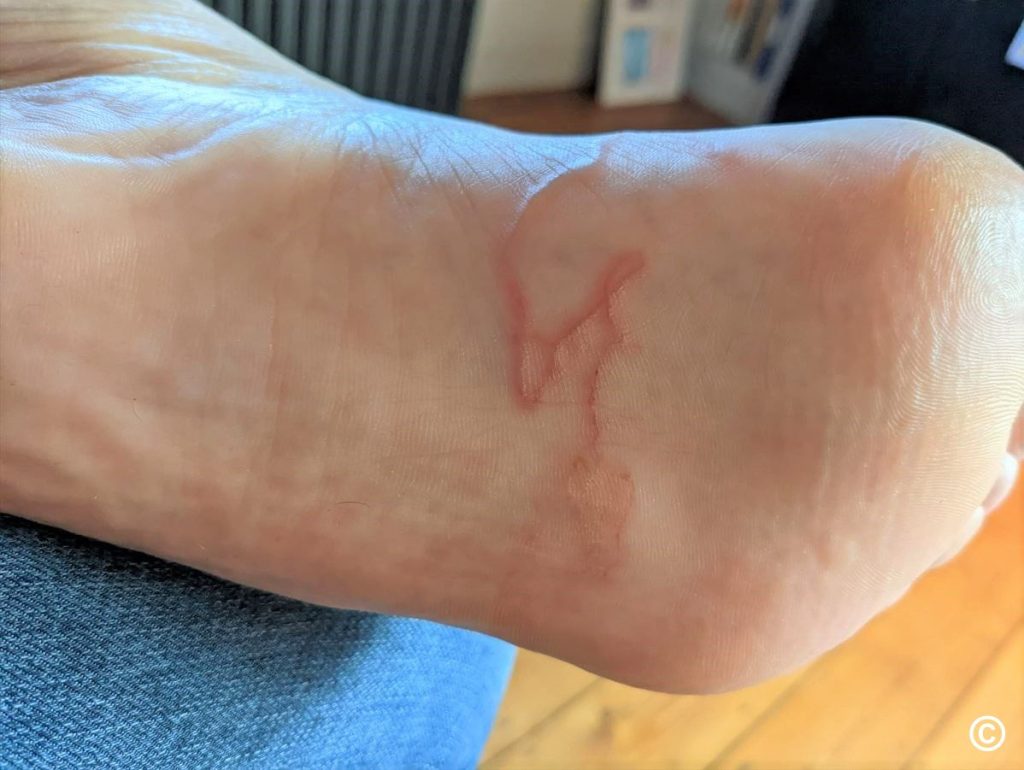
Larva Migrans
Larva migrans, also known as cutaneous larva migrans or creeping eruption, is a parasitic skin infection caused by the larvae of various types of hookworms, typically dog or cat hookworms. The larvae burrow into the skin, causing raised, winding, red or pink tracks that may be intensely itchy. Larva migrans is commonly acquired through contact with contaminated soil or sand, particularly in tropical or subtropical regions. Treatment typically involves topical or oral medications, such as antiparasitic drugs, to kill the larvae and relieve symptoms.
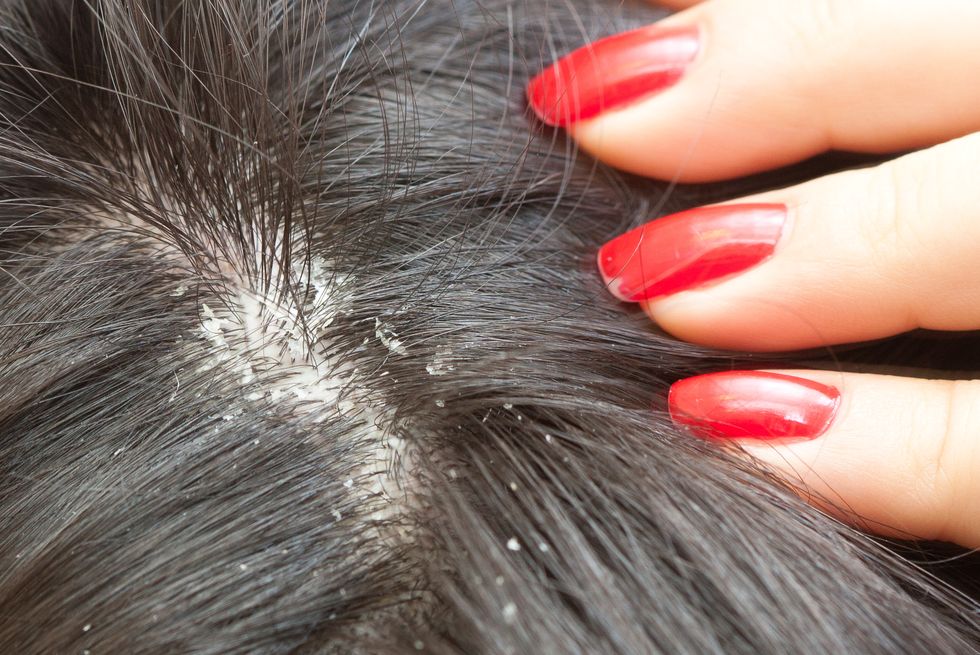

Dandruff
Dandruff, also known as seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, is a common chronic scalp condition characterized by flaking, itching, and irritation of the scalp. It is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, which is naturally present on the skin. Factors such as hormonal changes, stress, and certain skincare products can exacerbate dandruff. Treatment options include medicated shampoos containing ingredients such as zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or coal tar, which help control yeast growth and reduce flaking.
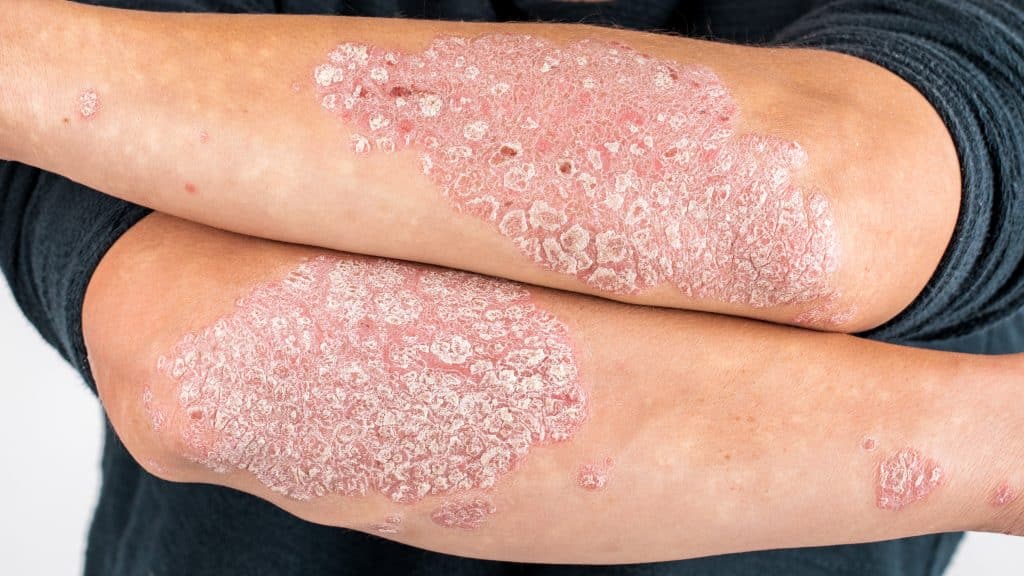
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches of skin, often accompanied by itching, burning, or pain. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid turnover and buildup of skin cells on the surface of the skin. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and nails. Treatment options include topical medications, phototherapy (light therapy), oral medications, and biologic therapies to reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
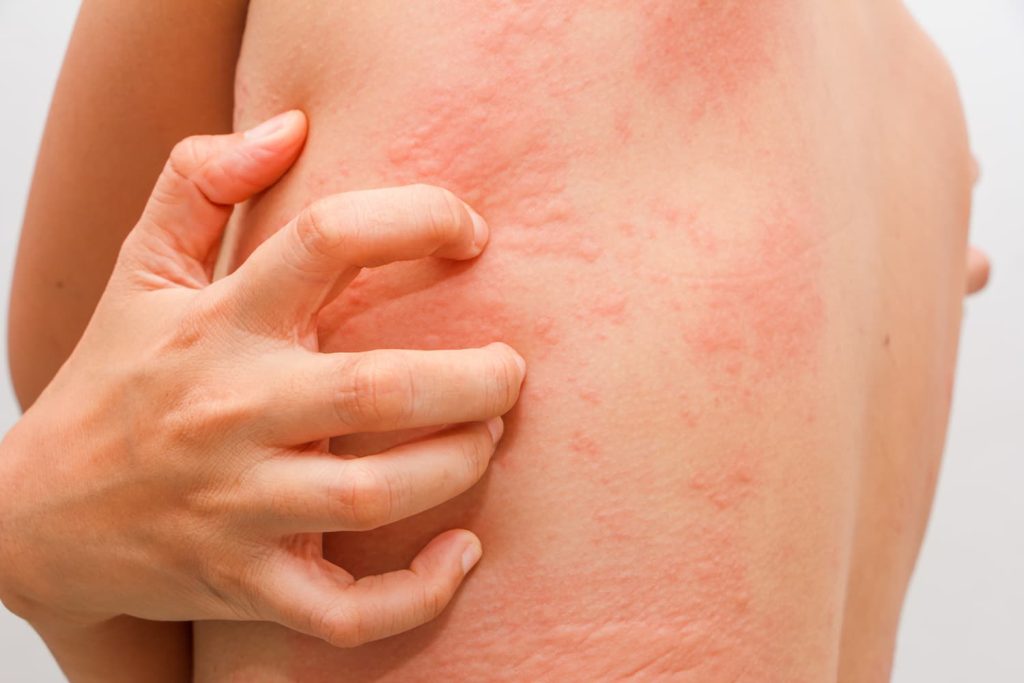
Urticaria
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts or wheals that can vary in size and shape. It occurs when the body releases histamine and other chemicals in response to allergens or other triggers, causing inflammation and swelling of the skin. Urticaria can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks). Treatment options include antihistamines to relieve itching and inflammation, as well as identifying and avoiding triggers to prevent recurrence.
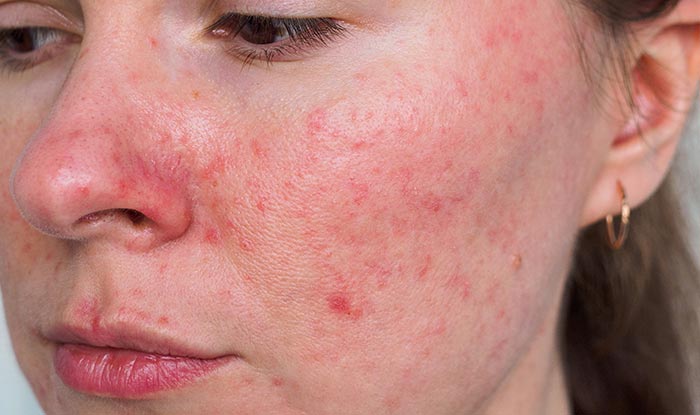
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by persistent facial redness, flushing, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia), and sometimes papules and pustules that resemble acne. It typically affects the central face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. The exact cause of rosacea is unknown but may involve genetic, environmental, and vascular factors. Triggers for rosacea flare-ups include sunlight, stress, spicy foods, alcohol, and certain skincare products. Treatment options include topical and oral medications (e.g., antibiotics, retinoids), laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
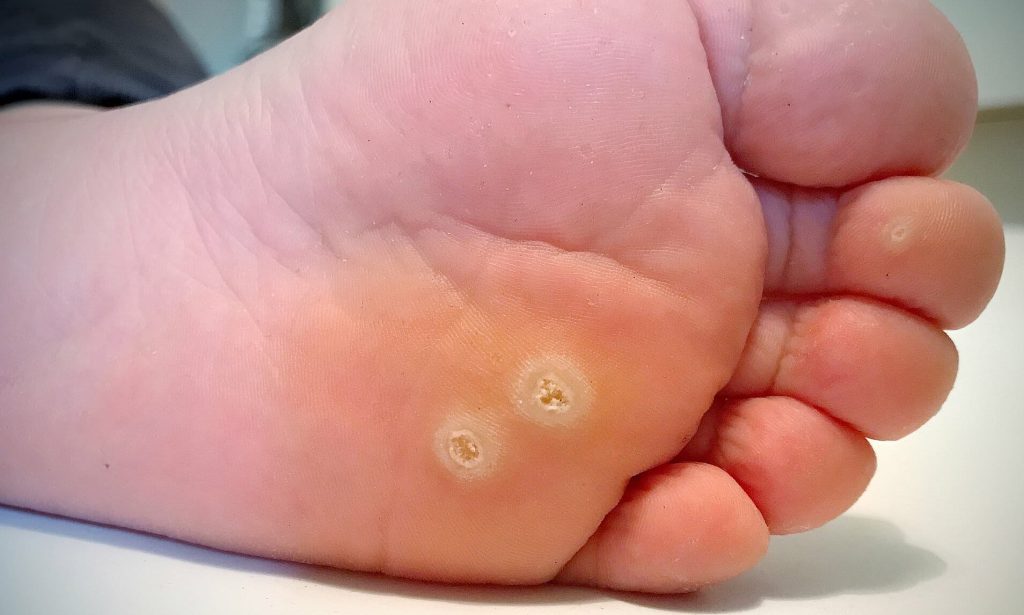
Warts
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which infects the top layer of skin and causes rapid cell growth. Warts can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the hands, feet, and face. They can vary in appearance, from small, rough bumps to larger, cauliflower-like growths. Warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces. Treatment options include topical medications (e.g., salicylic acid, retinoids), cryotherapy, laser therapy, or surgical removal to eliminate the wart and prevent recurrence.
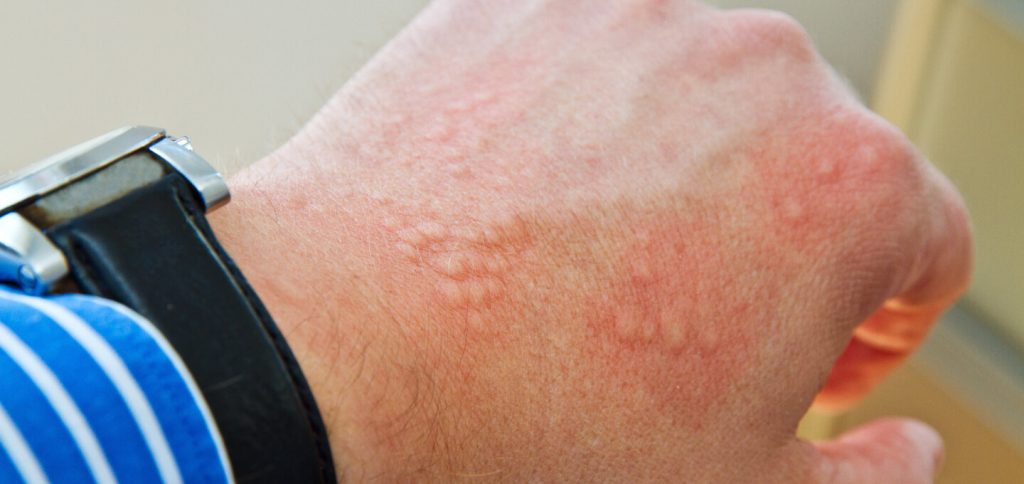
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with irritants or allergens, triggering an inflammatory response. It can manifest as redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering or oozing of the skin. Common irritants and allergens include soaps, cosmetics, jewelry, latex, plants (e.g., poison ivy), and certain medications. Treatment involves identifying and avoiding the triggering substance, as well as using emollients, topical corticosteroids, or oral antihistamines to relieve symptoms and promote healing.
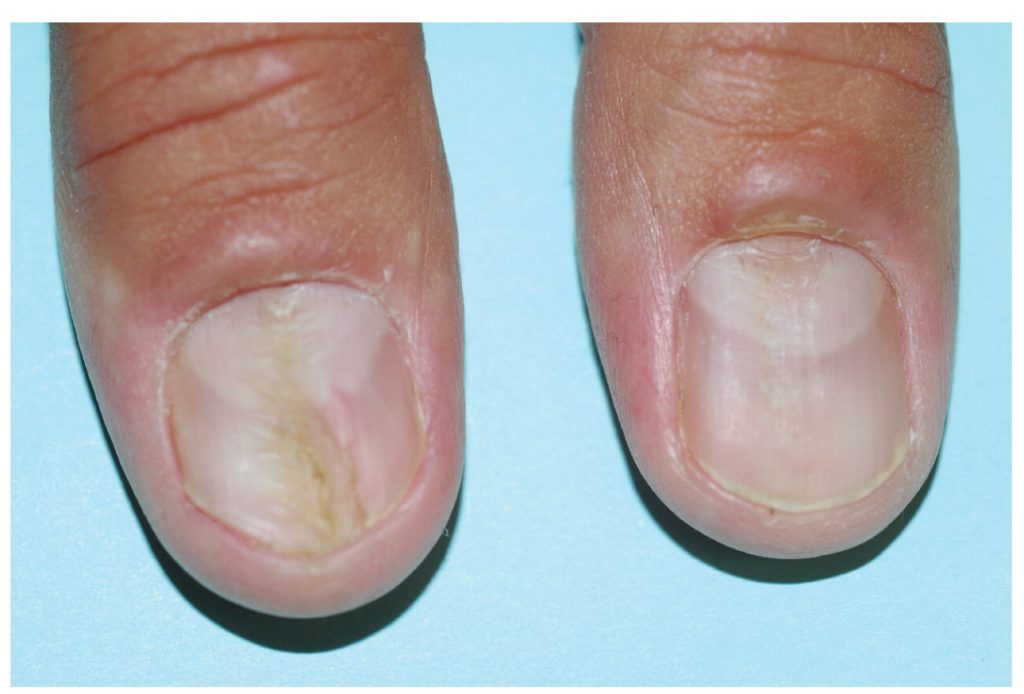
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis, commonly known as nail fungus, is a fungal infection that affects the nails, typically the toenails. It can cause discoloration, thickening, and brittleness of the nails, as well as separation of the nail from the nail bed. Onychomycosis is often caused by dermatophyte fungi and can be acquired through exposure to contaminated surfaces such as shower floors or shared nail grooming tools. Treatment options include oral antifungal medications, topical antifungal solutions, and in severe cases, surgical removal of the affected nail.
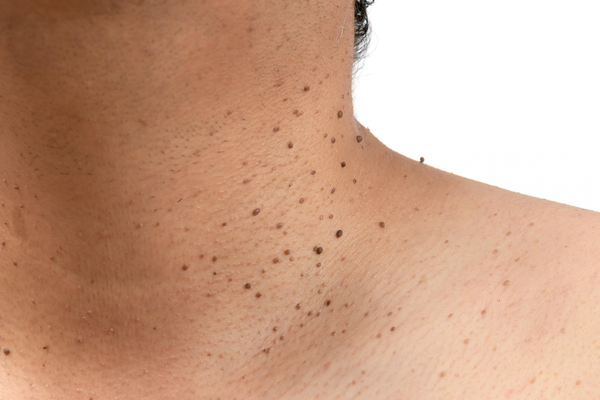
Skin Tags
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are small, benign growths that commonly occur on areas of the body where skin rubs against skin or clothing, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. They are typically flesh-colored or slightly darker and can vary in size. While skin tags are harmless and usually painless, they can be bothersome or cosmetically undesirable for some individuals. Removal options include cryotherapy , excision, or cauterization, which can be performed by a dermatologist or other healthcare provider.
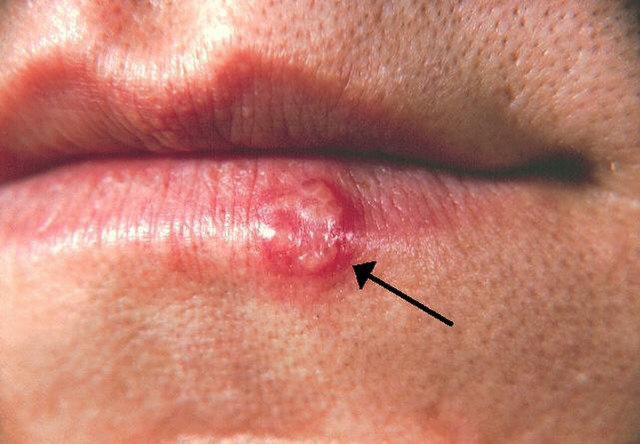
Herpes Virus
The herpes virus refers to a group of viruses that cause infections characterized by painful sores or blisters on the skin or mucous membranes. The two most common types of herpes viruses that affect the skin are herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 commonly causes oral herpes (cold sores), while HSV-2 typically causes genital herpes. Treatment options for herpes outbreaks include antiviral medications to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, as well as measures to manage pain and discomfort.
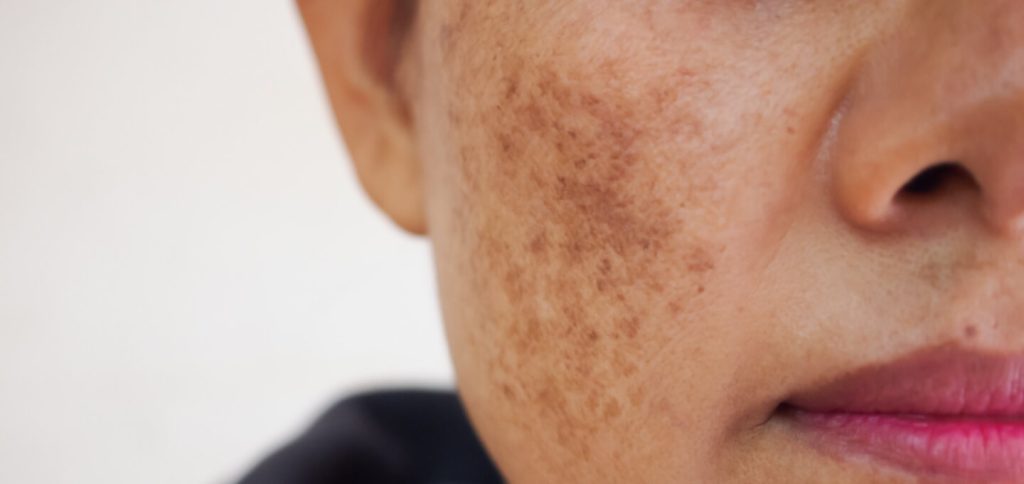
Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, irregular patches of hyperpigmentation on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, chin, and upper lip. It is more common in women and is often triggered or exacerbated by hormonal changes, sun exposure, or certain medications. Melasma is typically diagnosed based on the appearance of the skin, although a biopsy may be performed in some cases. Treatment options include topical depigmenting agents, such as hydroquinone, retinoids, and corticosteroids, as well as procedures like chemical peels or laser therapy to lighten the affected areas.
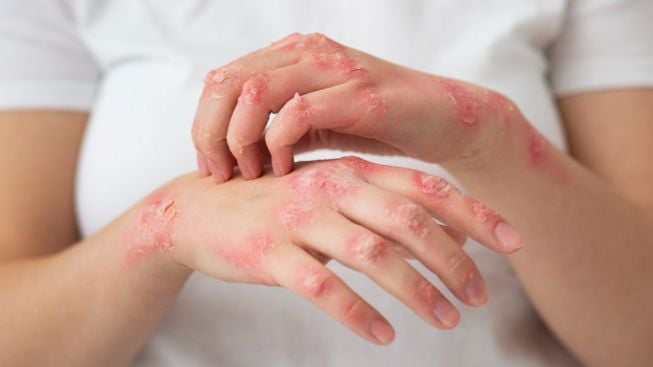
Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. It is characterized by intense itching, especially at night, and the appearance of small, raised bumps or burrows on the skin. Scabies is spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infested person and can also be transmitted through shared bedding or clothing. Treatment involves topical medications, such as permethrin or benzyl benzoate, applied to the entire body to kill the mites and eggs, as well as washing bedding and clothing in hot water to prevent reinfestation.
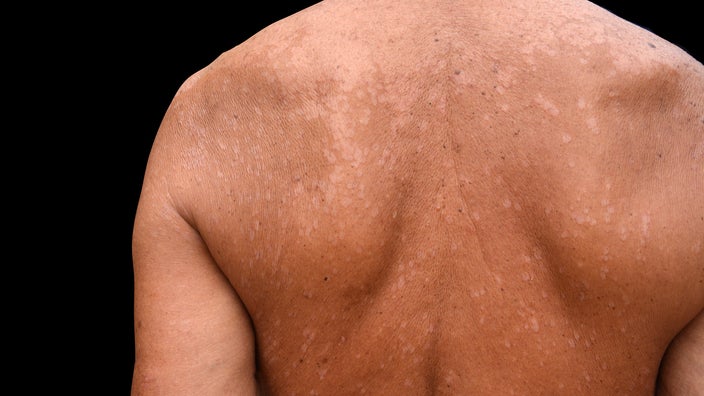
Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor, also known as pityriasis versicolor, is a common fungal infection of the skin caused by the Malasse.
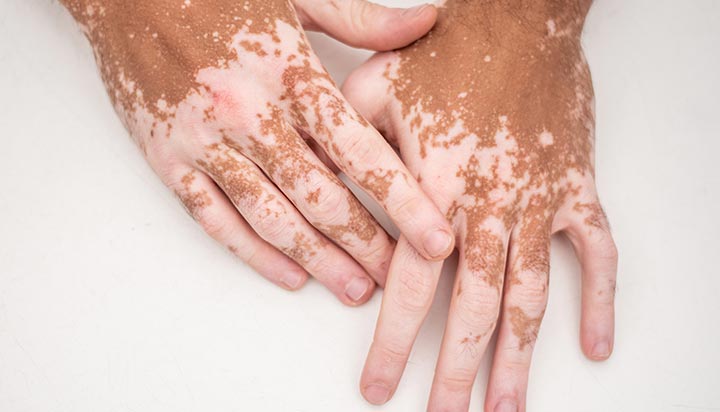

Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a chronic skin disorder characterized by the loss of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes), resulting in white patches or depigmentation on the skin. It can affect any part of the body, including the face, hands, feet, and genitals. The exact cause of vitiligo is unknown, but it is believed to involve autoimmune, genetic, and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, and surgical procedures such as skin grafting or melanocyte transplantation to restore pigmentation.
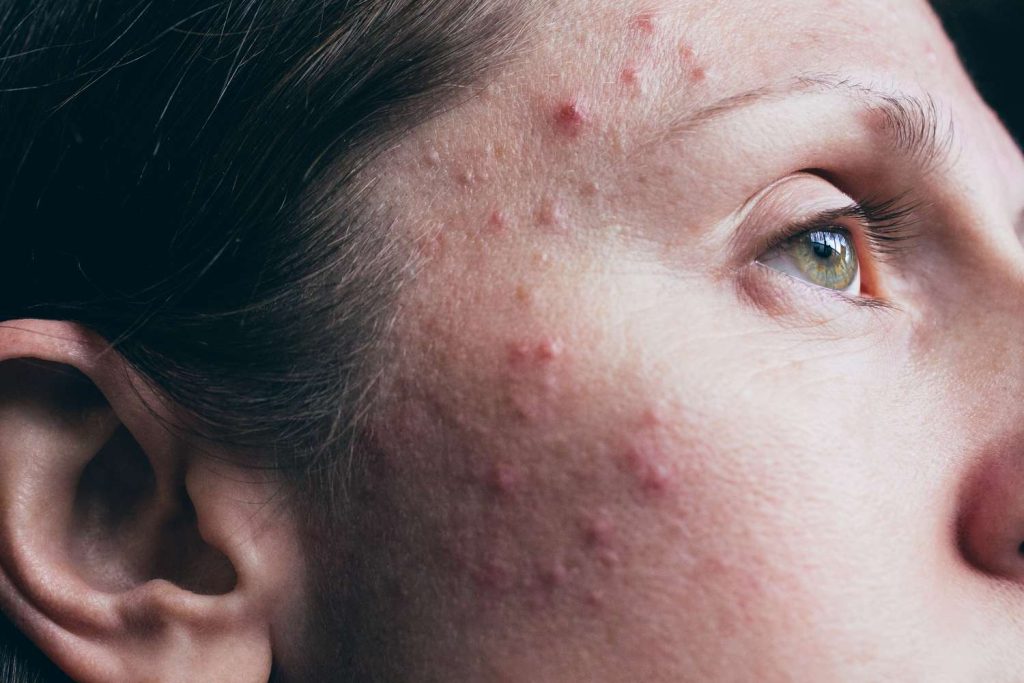
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts or nodules on the skin. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria and inflammation. Acne can affect people of all ages but is most common during adolescence due to hormonal changes. Treatment options include topical medications (e.g., benzoyl peroxide, retinoids), oral medications (e.g., antibiotics, hormonal therapy), and procedures such as chemical peels or laser therapy to reduce acne lesions and prevent scarring.
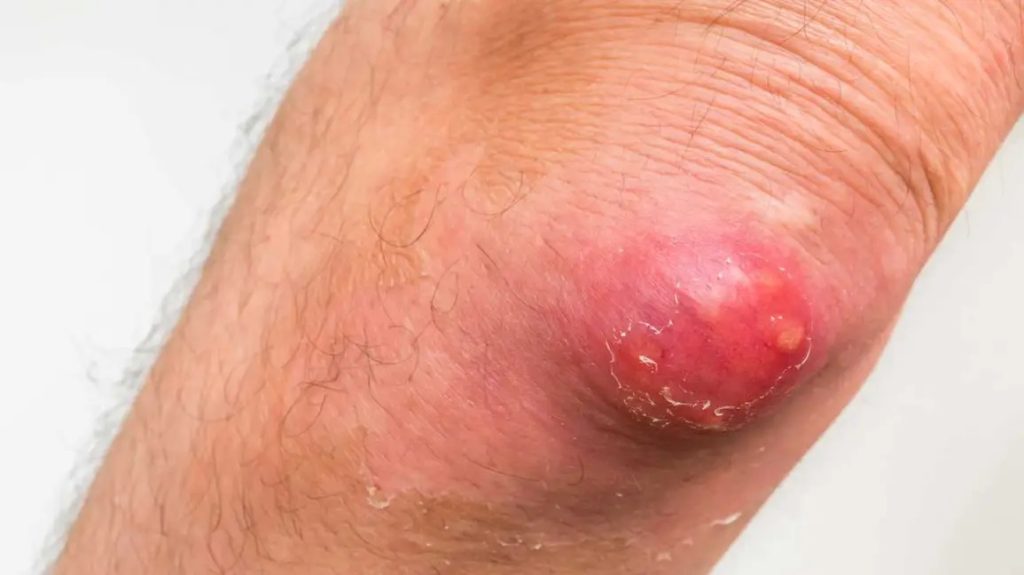
Carbuncle
A carbuncle is a deep-seated skin infection caused by bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus, that affects multiple hair follicles. It appears as a painful, swollen, and inflamed mass or lump with pus-filled lesions. Carbuncles typically develop on the back of the neck, shoulders, or thighs and may be accompanied by fever and fatigue. Treatment involves drainage of the carbuncle to remove pus and debris, along with antibiotic therapy to eliminate the bacterial infection. In severe cases, surgical incision and drainage may be necessary.
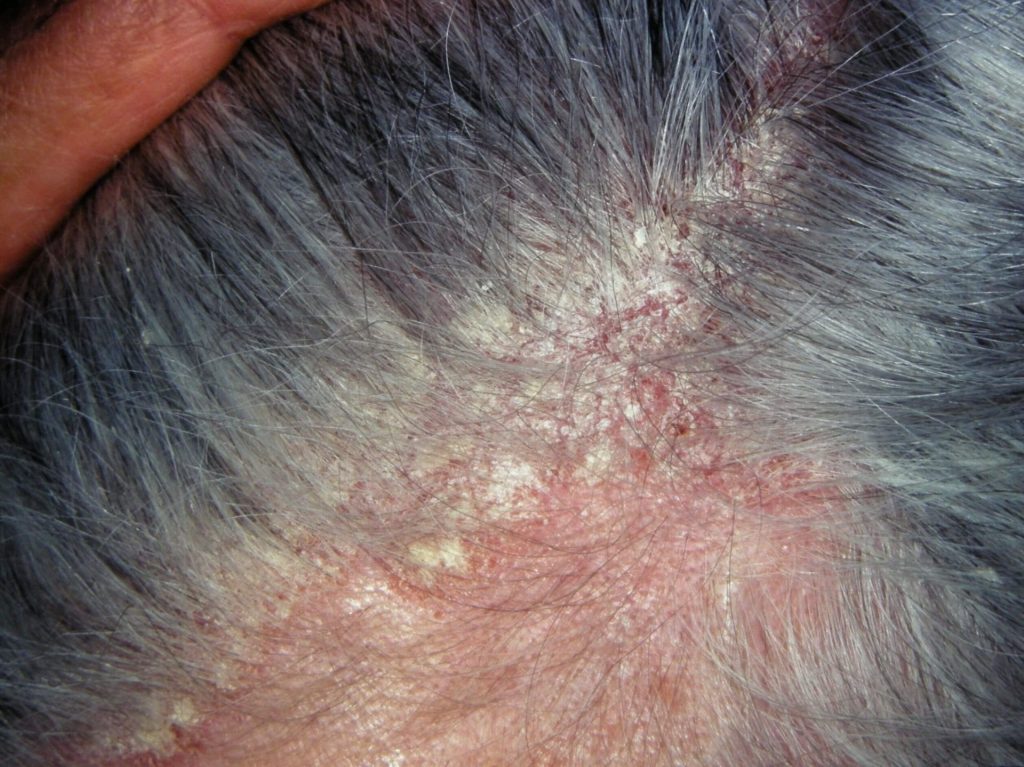
Seborrheic Eczema
Seborrheic eczema, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, is a common inflammatory skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and flaking of the skin, particularly in areas rich in sebaceous glands such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and microbial factors, including the yeast Malassezia. Triggers for seborrheic eczema flare-ups include stress, cold weather, hormonal changes, and certain skincare products. Treatment options include medicated shampoos containing antifungal agents or keratolytics, topical corticosteroids, and antifungal creams to reduce inflammation and control symptoms.
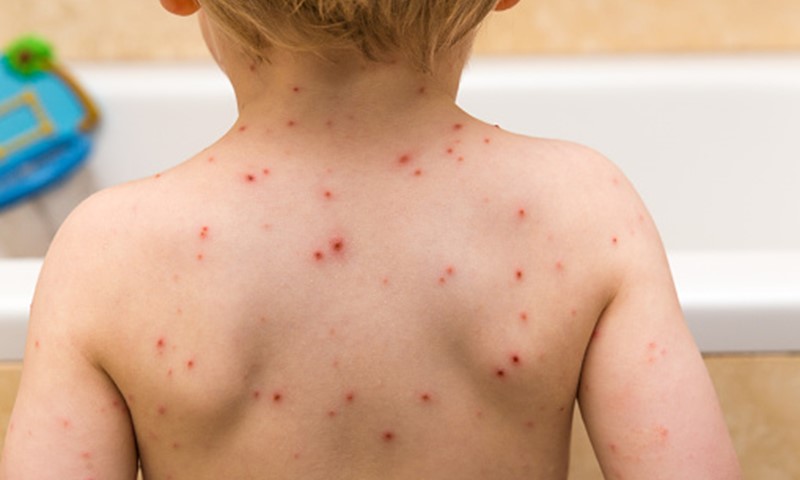
Chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is characterized by an itchy rash of small, fluid-filled blisters that can appear anywhere on the body, along with fever, headache, and fatigue. Chickenpox is spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with the fluid from the blisters of an infected person. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms such as itching and fever, as well as preventing complications such as bacterial skin infections. Vaccination with the varicella vaccine is highly effective in preventing chickenpox.
